Computational Modelling of the Installation Process of a Semi-flexible Kevlar Reinforced Composite Liner in Offshore Pipelines
Abstract
Internal corrosion in pipelines is a persistent problem in the oil and gas industry. Available conventional rehabilitation techniques to prolong the life of the pipeline use an internal lining system to isolate the corrosive medium from the host pipe’s inner surface. To overcome many of the shortcomings associated with conventional lining technologies, a Kevlar-reinforced flexible polymer composite liner (IFL) has been recently developed. This flexible liner was installed in several stages and is of interest in understanding the mechanisms behind the installation process and, more specifically, determining the forces and stresses at each stage of the installation process. In the current study1,2 a nonlinear finite element modelling framework is presented, as shown in Fig. 1, to simulate the full installation process of the IFL. The FE model is further validated using physical tests, making it a reliable tool for simulating the entire installation process composite liners and RTPs.
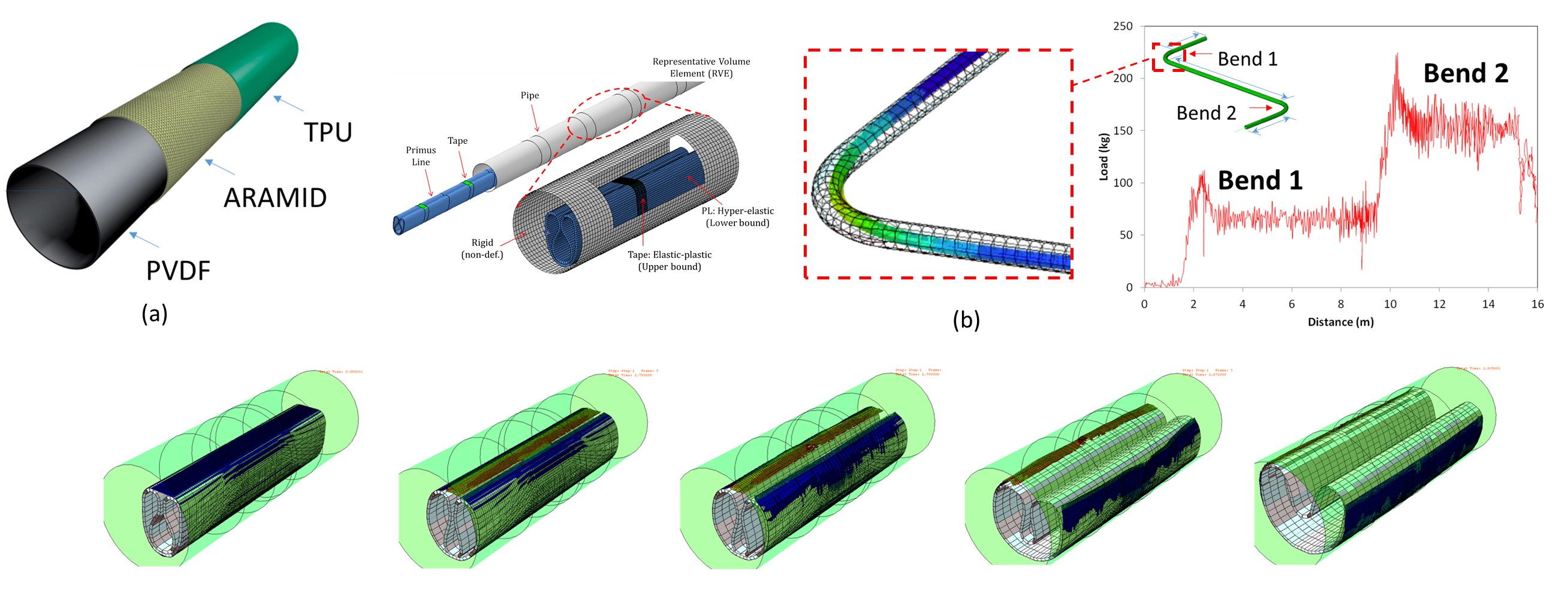
Figure 1: (a) The In-Field Liner (IFL), (b) pull-in of the tape wrapped IFL through a steel host pipe, and (c) inflation of the IFL inside the steel host pipe1.
References
- Barsoum, I., Dymock, J., Walters, R. and Seibi, A., “Finite Element Analysis of the Installation Process of a Novel Corrosion Protective Kevlar-Reinforced Flexible Composite Liner”. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract., Vol. 9, Issue 4, (2018).
- Fahed, M., Barsoum, I., Alfantazi A., Islam, M.D., “Integrity Assessment of Internally Corroded Pipelines Rehabilitated With a Kevlar-Reinforced Flexible Liner”. J. Press. Vessel Technol., vol. 142, issue. 4, (2020).
Location: Building 19, Level 3, Hall 1-2.
Speakers
Imad Barsoum
Professor at Khalifa University